I was first introduced to Kinesiological (Kinesio) style taping during a continuing education class in 2005. Since then, this style of taping has exploded in the mainstream with athletes and celebrities alike wearing it. Research on this modality was initially scant. Today there are over 540 published studies with even more antidotal testimony! Although the research is ongoing and published regularly, I get asked all the time about what can you use Kinesiological tape for and how exactly it works. I will review three theories on how Kinesiological tape actually works and the different reasons for using it.
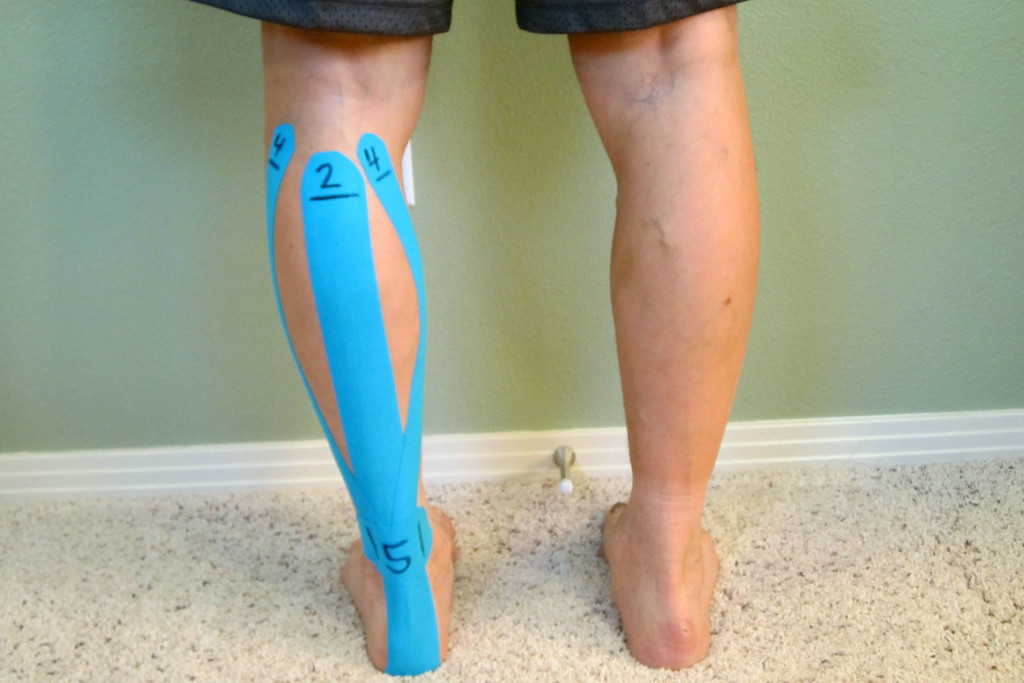
Kinesiological Taping For Achilles Tendinitis
How does Kinesiological Tape Work?
- Sensory Theory (also known as the Gate Control Theory) – The basic premise of this theory is that the Kinesiological tape, when applied to the skin, activates sensory receptors present on the skin. These receptors relay information to/from the brain. Since the sensory receptors are faster than other types of receptors (such as pain) the brain reacts to the sensory information first. This can lead to altered movement patterns and awareness to the area. It can also allow for decreased sensations of pain. This theory is similar as to why we think topical analgesics (such as Biofreeze) work as well as why transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS units) can reduce pain.
- Circulatory Theory – The basic premise of this theory is that the when the Kinesiological tape is applied with little tension it forms convolutions in the skin. These convolutions create channels and reduce pressure within the tissues, lymph system, and circulatory system which aids in blood and lymphatic flow.
- Muscle Activation Theory – The premise of this theory is that when the Kinesiological tape is applied at different levels of tension on the skin over the muscles and tissues, the Kinesiological tape can either mechanically or neurological increase or decrease muscle activation via a nervous system response.
Presently the truth behind Kinesiological taping is that we really don’t know exactly how or why it works. Based on my clinical experience, I believe that the Kinesiological tape interacts with the body’s tissues in different ways depending on how and where the Kinesiological tape is applied. Depending on how the Kinesiological tape is utilized, any one or combination of the three theories is likely correct.
Research states that Kinesiological style taping is at least as effective as other minimal interventions for musculoskeletal pain which may include topical analgesics like Arnica montana (Arnica Rub) or Biofreeze.
Research has also shown that taping can reduce pain acutely within first week of injury and possibly even in cases of pain which has been present for as long as three to four weeks (or longer).
Research concludes that there are some improvements in muscle and joint range of motion (ROM) and a reduction of pain. However, because the improvement isn’t significant or long standing it shouldn’t be used as a standalone intervention. Kinesiological taping is best used in combination with other interventions (such as manual therapy based techniques and exercise) which have been proven to affect outcomes over the long-term.
When Kinesiological tape is used in conjunction with other treatments, it may help speed up the recovery as the Kinesiological tape can allow for other techniques to be utilized more effectively due to the loss of pain, swelling or easing of movements.
Although there have been hundreds of research studies performed, the effectiveness of Kinesiological tape is still questioned primarily due to issues with research design. Many of the taping applications are based on theory and not science. Since there isn’t a consistent application pattern, the research studies aren’t comparing the same techniques over large enough patient populations to show a true effect. In addition, researchers still need to quantify how much tension is actually being used and the actual Kinesiological taping technique being used versus other types of techniques or interventions.
Unfortunately, without better quality research it’s unclear if the results shown in many of the studies are due to an actual effect or through placebo. For now, none of the studies show significant benefits regarding long-term pain alleviation or improved strength or range of motion (ROM). So for now, the main conclusion is that Kinesiological taping should be used only as a short-term treatment in combination with other treatments. I personally use Kinesiological tape, and I often find that my clients experience success with specific tape applications for different conditions.
What do you use Kinesiological Tape for?
- Reduce pain
- Reduce swelling and edema
- Support muscles and joints
- Reduce muscle tension
- Increase strength
- Improve performance
- Enhance or correct movement patterns through stimulation of sensory receptors
- Provide compression
- Enhance healing by slightly lifting skin away from sore or injured tissues to improve blood flow and lymphatic drainage
- Support injured joints and muscles without impeding range of motion (ROM)
There are dozens of companies’ now manufacturing Kinesiological style tape. There are many high quality tapes being manufactured with all kinds of colors, designs, and variations in adhesive quality and elasticity. Personally, my favorite brands are based on price point and actual use. This includes ease of application and how long the Kinesiological tape actual stays on. The brands I use most include: Kinesio Tape, RockTape, Thera-Band Kinesiology tape, Spider tape, and KT TAPE. Although there are many more brands available, I have not personally used them.
There are many different applications Kinesiological taping can be used for. Like any treatment modality, it can work wonders for one person and do nothing for another, but should we really be surprised? Many of our most popular pharmaceuticals are no different. Kinesiological taping has the benefit of rarely having significant side effects. There are rarely side effects to utilizing this style of tape as the products utilized tend to be very hypoallergenic. Occasional skin irritation has been the only noted side effect I have known of in my clinical experience. In order to avoid skin related issues (including application and removal tips), please refer to Skin Care with Taping.
I have found success with utilizing Kinesiological taping as an adjunct treatment strategy and as part of a complete treatment approach. If you are interested in specific applications for different conditions, please see the following in which I demonstrate different taping techniques.
Step-by-step guides:
Kinesiological Taping for Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Kinesiological Taping for Patellar Femoral Pain Syndrome
Kinesiological Taping for Shin Splints
Video:
How to Apply Kinesiological Tape When Treating Achilles Tendinitis
Books with step-by-step guides specific for ankle sprains and low back pain:
The Physical Therapy Advisor’s Guide to Treating Ankle Sprains and Strains
The Physical Therapy Advisor’s Guide to Treating Low Back Pain During Activity and Exercise
Have you tried using Kinesiological taping before? If so, what was your experience like, and did it help you? Please leave your comments below.
If you have a question that you would like featured in an upcoming blog post, please comment below or submit your question to contact@thePhysicalTherapyAdvisor.com. Be sure to join our growing community on Facebook by liking The Physical Therapy Advisor!